Blockchain - is it a change as big as the Internet revolution?
New solutions carry many promises, but also fears. The history of the blockchain begins with the beginnings of bitcoin. Cryptocurrencies have aroused mixed emotions from the moment of emergence, dividing the cryptocurrency community into both their strong supporters and strong opponents. Blockchain also provokes considerable interest among representatives from outside the IT industry.
And what is blockchain actually? Literally explaining, it is a chain of blocks through which transactions are carried out. Each block is an important element in which there is a certain amount of data. They depend directly on the protocols, which in turn are assigned to specific transactions. An example of a protocol is bitcoin or ethereum itself, which in turn consist of a cryptographic method, peer-to-peer network and proof of work. All this is a set of rules that allow devices to connect and exchange data. The best example of a protocol to illustrate it is TCP / IP – the progenitor of today’s Internet.
Blockchain is the future for international transactions, which has a chance to replace currently available solutions – such as international payments or financial transactions. Solutions based on block chains or codes are increasingly used in other areas of life. An example is the operation of the Swiss canton Zug, which plans to conduct a trial vote, using blockchain technology. It is true that the issue in which the referendum is prosaic – it is about fireworks, but nevertheless it has to use the urban eID system and the application for mobile devices.

source: blockchainage.com
What sets blockchain apart from traditional solutions is:
- Supporting the entire solution on cryptography. The encoded cryptographic structure is self-verifiable and does not need the third party to obtain confirmation. As a result, blockchain performance is increased while costs are reduced.
- Transparency of action, which is the basis of clarity and security.
- Decentralization that allows you to protect against system failures.
- In addition, the “chain block” register is public – the availability of information is common and unlimited, public, anonymous – the registers do not contain information about who owns, for example, bitcoin portfolio and is not subject to the control of a single entity.

source: pixabay.com
These advantages are a component of the value directly related to the idea of the Internet of Things. It aims to collect, process and exchange data. The genesis of the blockchain is based on the exchange – services, goods – which becomes the basis for the economic functioning of society.
Blockchain technology and its development are heading towards the free dimensions creating a kind of revolution – as it was seen in the creation of a global network, which is the Internet. Similarly operate businesses based on partner networks. Such examples may be eBay or Polish Allegro, which bring users together in one place. On the other hand, a single contractor, regardless of the entire network, determines the terms and the amount of the transaction. The most important element in this exchange is the transaction itself, and not the payment instrument – as it does in the case of bitcoin, based on blockchain technology. Similarly, we can deal with the exchange of data; where the most important will be their effective and fast exchange, not the form of this information (data).
IoT in combination with blockchain has already found application mainly in the exchange of cryptocurrencies. Some countries are going a step further, where such solutions can also be found, among others in securing medical data – authentication and verification of access in Estonian health care. It is also used in the creation of smart contracts, where the process of activating automatic payments is based on network compliance .
AWS as a leader in modern solutions based on cloud computing, also provides its clients with solutions based on this technology. Two examples of templates with their use are described below.
AWS Blockchain Template for Ethereum is a template that uses Solidity framework. Solidity is a high level language that allows you to implement something called Smart Contract. Smart Contract – on the one hand, it preserves the confidentiality of parties participating in it, and on the other, it defines terms of the agreement between the parties using one protocol (API), minimizing the risk for the parties to the contract. This template can be used, for example: to build a crowdfunding platform, a voting page or blind auction etc.
HyperLedger Fabric, again this is a framework that uses blockchain technology. It was built by TLF (The Linux Foundation), with considerable input from IBM. It has modular architecture. It is easily extensible and uses container technology. What can you use it for? It can be used to create a “distributed ledger”. Distributed ledger can be compared to a distributed database in which there is no master and all pages have copies of information, but none of the parties alone, without the consent of the others, can make modifications (this is determined by the consensus protocol). “Base” works in “append only” mode. Access to the database is determined by smart contracts. It is used in enterprise class solutions.
Differences that we can see between the two mentioned templates appear in the language used to create them and build them.
The following diagram shows the components of a block network on AWS, created using the aforementioned templates. An example scheme for using such a template is presented below.
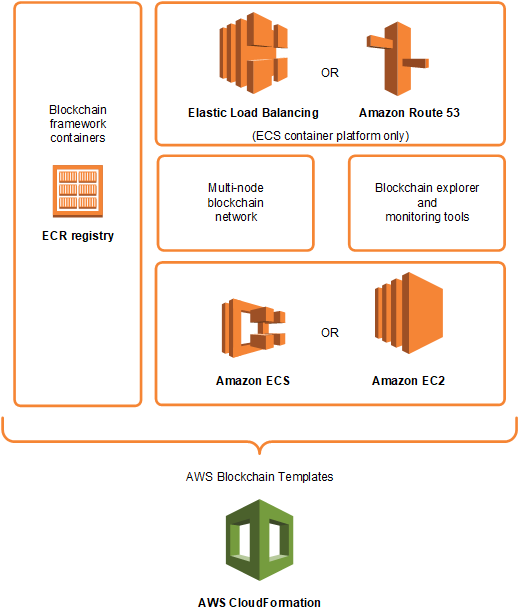
source: Amazon Web Services
Building specific solutions based on blockchain in AWS can also be enriched with such solutions as Amazon Kinesis Data Firehose, Amazon Kinesis Data Analytics, Amazon Kinesis Data Streams or Amazon Athena.
An interesting case was described by Dr. Jonathan Shapiro-Ward (AWS Solutions Architect) on AWS’ blog, which we recommend to look at.
The diagram below shows the outline of the use of these services.
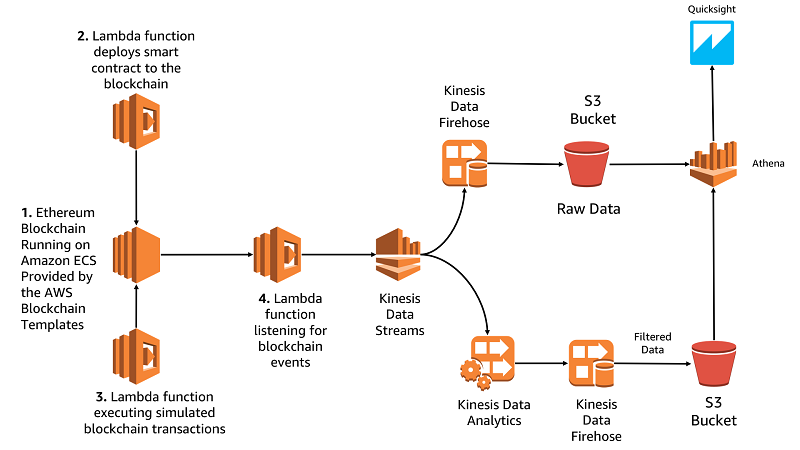
source: Amazon Web Services
At present, blockchain is in an extremely dynamic phase of development. Its innumerable advantages affect its great attractiveness. Solutions based on block or code chains are used in many industries, where the priority is safety and ensuring the highest quality of services. For those who would like to delve into this subject, we recommend the text from Mohit Mamori – a great enthusiast of blockchain, who in an accessible way shows the operation and application of this technology.
Used sources:
