Cost optimization in Google Cloud
Managing expenses in the cloud is one of the most important issues when designing a cloud solution. The application of appropriate principles of good design will allow not only to ensure high availability of the solution but also to meet the demand and optimize the control of operating costs of the environment.
Monitoring costs is not an easy task, even if it seems so obvious that we are paying for cloud resources available on demand. To properly optimize your expenses, you first need to understand the essence of cost generation. For this, cost management and accounting tools will be useful. Billing reports that give you an insight into costs are also useful. An important activity is the appropriate tagging of assigned costs for individual departments. The use of labels allows you to create personalized dashboards with the necessary information. You can also use quota, budgets and alerts to accurately control costs. They make it possible to monitor trends and forecast them over time, taking into account possible differences in the budget.
Once you have knowledge of the tools, the next step is to identify resources that are not delivering business value to your organization.
The first thing that will lower costs will be identifying idle virtual machines (VMs) and disks and cutting back on resources that are not being used. To this end, Recommender was created, which identifies inactive virtual machines (VMs) and hard disks based on usage rates. Keep in mind the consequences of removing resources; deleting an instance removes the underlying disk (s) and all of its data. It is good practice to snapshot the instance and the alternative is only to stop the virtual machine, which in turn will save resources.
The second consideration is scheduling the startup and shutdown of virtual machines. Production systems usually run 24/7. But virtual machines in development, test or personal environments are usually only used during working hours. Therefore, their exclusion may contribute to considerable savings. A solution specially prepared by GCP Team, based on the Serverless technology, will be useful here, which will allow automating the process of automatic shutdown of virtual and large-scale management machines.
The third issue is the appropriate type (size) of virtual machines (VMs) – the so-called rightsizing. Custom Machine Types is a functionality of the Compute Engine service that allows you to easily create machine types tailored to your current needs. One last issue related to virtual machines; you should also consider instance options, which operate on a 24-hour basis and are generally up to 80% cheaper than long-term solutions. Preemptible VMs are suitable for fault-tolerant workloads such as big data, genomics, media transcoding, financial modelling, and simulation. Thanks to the appropriate plan and the Flexible Resource Scheduling tool, you can reduce the costs of stream and batch analysis.

Storage, data storage, and cost management can all disappear into the total cost of infrastructure management. However, in the cloud, where storage is billed as a separate item, paying attention to its usage and configuration can result in significant savings.
Here are 3 rules that can help you save space, time, and storage costs.
- Cloud Storage classes. Each of the available classes has a specific use and price list. Appropriate use of the class for its intended purpose allows you to optimize expenses. By using, for example, the coldline or archive type, you can significantly reduce the cost of storing data, access to which is not needed often.
- Lifecycle policies. Appropriate use of classes in conjunction with the automation of facility lifecycle management can reduce the costs of data archiving. Object lifecycle configuration should be adapted to the object’s storage class, based on a set of conditions, or include its complete removal if not needed.
- De-duplication. Another cost-generating issue is the duplication of stored data. Of course, there are situations when duplication is required, e.g. by a team working in different regions, who needs immediate access to data. So it makes sense to create a multi-region bucket, rather than having multiple copies in different containers. You should also read about object versioning in Cloud Storage. Appropriate configuration prevents overwriting or accidental deletion of data.
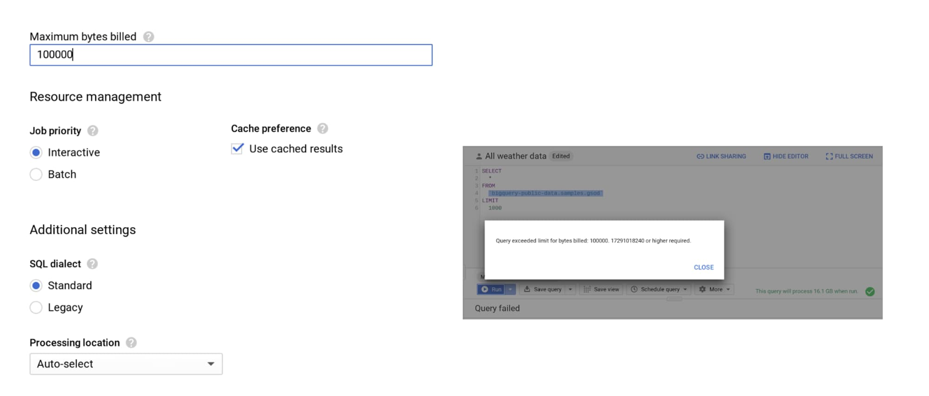
Another useful service when optimizing costs is BigQuery, which allows for a modern approach to data analysis and appropriate configuration, and as a result allows you to reduce costs. The first point is query control, which will allow you to monitor your accruals. For this, it will be useful to set the limits (maximum number of bytes). This will allow for supervision, and exceeding the set threshold will not cause additional costs – as it is shown in the example below:
It’s also worth taking advantage of table partitioning and clustering. Partitioning allows a table to be partitioned based on: processing time, date, time stamp, or a column of an integer range. By using the Require partition filter, you can make sure that your queries and tasks use partitioned tables. An additional advantage of using partitions in BigQuery is the ability to reduce data storage costs by 50% for each partition or table. Non-editable tables are moved to long-term memory, and simply moving a table or partition has no effect on performance, durability, availability, or degradation of functionality. At this point, let’s pay attention to data transfer/upload. Data can be uploaded to the BigQuery service in two ways:
- using bulk (batch) uploading,
- as part of streaming, in real-time – using streaming insertion.
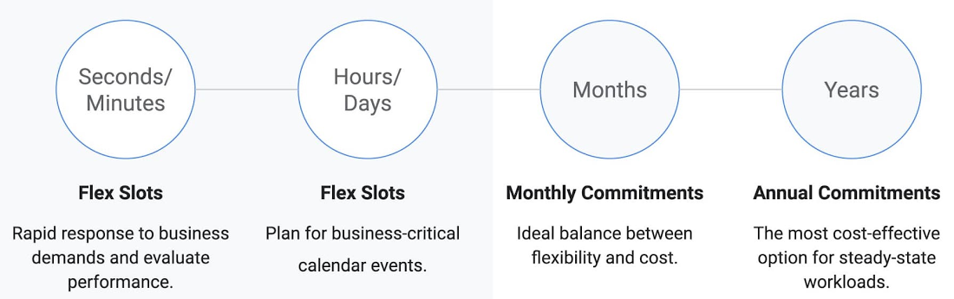
When analyzing the BigQuery account, it is important to determine whether the transferred data must be available immediately or whether it is used immediately in real-time. If not – it is recommended to use the first method of data upload, which is simply free. The last aspect worth paying attention to with BigQuery is billing based on the bytes used. The most commonly used option is on-demand pricing. This scenario will work for small amounts of data. However, when we have large volumes with stable loads, rate pricing will be more advantageous, which allows you to process an unlimited number of bytes at a fixed price. In order for the customer to cope with the right choice, Google has introduced the Flex Slots option for BigQuery, which allows the purchase of BigQuery slots for a period of only 60 seconds, in addition to monthly and annual lump sum commitments.
Finally, a few best practices related to logging and monitoring resource consumption in the cloud. They are the foundation when it comes to network operations and security.
- Check how much you spend on specific services and use Cloud Platform SKUs. Explore the network topology that will benefit from Network Topology with the Network Intelligence Center, providing visibility into global GCP deployment and public Internet interaction. Thanks to this, we are able to identify ineffective implementations and take the necessary actions to optimize the costs of traffic coming from the regional and intercontinental network.
Determine what level of network service you need. Google Cloud allows you to choose services on two levels: standard and premium. The premium option provides the highest performance, while the standard option can be an excellent alternative for high cost-sensitive workloads.
- Control network traffic. In the cloud you have access to network traffic, filtering logs that you no longer need. Data access control logs are important, the use of which may generate additional costs. And for VPC flow logs and cloud load balancing, you can also enable sampling. This can result in a significant reduction in the amount of log traffic that is written to the database.
Smart cost management in the cloud will allow not only their optimization but also the development of best practices for a given organization, regardless of whether it is a startup or a global enterprise. It is also worth seeing the video series on cost management in the cloud prepared by the GCP team. We also encourage you to browse the documentation yourself. individual services, which is updated on a regular basis.
If you are interested in the optimization of cloud computing costs in your company or you want to use the free USD 300 to check your idea on Google Cloud Platform, write to us at kontakt@lcloud.pl.